ALS Stem Cell Treatment
Stem Cell Treatment for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
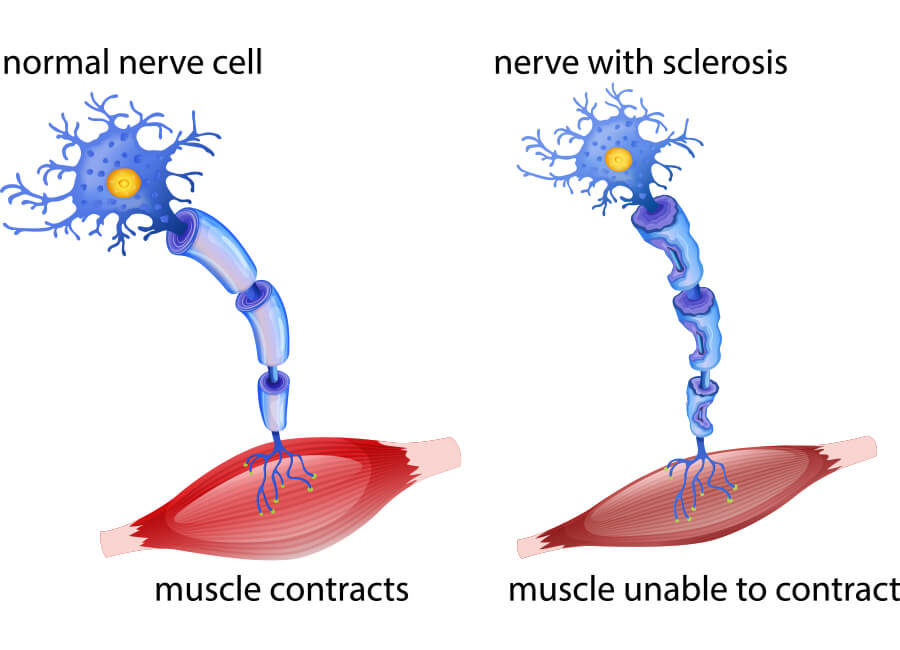
Stem Cell ALS Treatment: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a rare neurological disorder which is mainly related to nerve cells. Our neurons are responsible for muscle movements, like chewing, talking or breathing, just to name a few. It is a severity disease which means it will be increasing over the course of time. ALS Stem Cell Therapy is available now at our treatment center in Bangkok, Thailand.
Stem Cell ALS Treatment
ALS Stem Cell Therapy
There are no single tests that can detect ALS. The physician has to review the medical history and then conduct neurological examinations periodically to check whether the symptoms are getting worse or not. The primary diagnosis is made by observing the signs and symptoms by the physician after running a series of tests. These tests can be electromyography (EMG) wherein the electrical ability of the muscle fibers is checked through special recordings. Then there is Nerves Conduction Study (NCS) and this test is done on the nerves. The doctor may also refer to Magnetic Resonance Test (MRI) including a set of laboratory tests such as urine and blood tests.
MSC´s have plasticity properties and the ability to provide growth factors which modulate the immune system. The transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) leads to the increase in the survival of neurons as these cells are known to produce proteins that are helpful in the growth and survival of new-developing and mature neurons. Moreover, the idea of replacing the dying neurons with new stems cells is now more realistic, feasible and appealing. Patients who have been treated with stem cells have shown improvements in coordination, balance, speech, swallowing and few other areas as well.
Beneficial Actions of Stem Cells for ALS
- Ross the endothelial brain barrier
- Migrate to sites of injury (chemotaxis)
- Communicate with and alter nearby cells (paracrine effect)
- Encourage existing cells to self-repair (autocrine effect)
- Immune modulation
- Transform into neurons and glia
- Promote the formation of nerve cell axons (axogenesis)
- Release neuroprotective factors
- Encourage existing cells to adapt (neuroplasticity)
Results Achieved with Stem Cell Treatment for ALS:
- Slowing of disease progression
- Improved breathing ability
- Improved speech
- Improved ability to swallow
- Reduced levels of muscle wasting
Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment Mode of Action and Therapeutic Benefit for ALS
Mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) treatment has shown promise as a potential therapeutic approach for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). While the exact mode of action is still being studied, several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the therapeutic benefits of MSC treatment for ALS. These include:
Anti-inflammatory effects: MSCs have immunomodulatory properties and can suppress inflammation in the central nervous system. In ALS, neuroinflammation contributes to the progression of the disease. MSCs release anti-inflammatory molecules and regulate immune cell responses, thereby reducing inflammation and protecting motor neurons.
Trophic support: MSCs can secrete various growth factors, such as brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). These factors promote the survival and growth of neurons, enhance neuroprotective mechanisms, and support the survival of motor neurons affected by ALS.
Modulation of oxidative stress: Oxidative stress plays a role in the progression of ALS. MSCs possess antioxidant properties and can reduce the harmful effects of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on motor neurons. They secrete antioxidant enzymes and molecules that counteract oxidative damage, thus protecting neurons from further injury.
Immunomodulation: In ALS, immune dysregulation contributes to the neurodegenerative process. MSCs can modulate the immune response by suppressing harmful immune cells and promoting the activity of regulatory immune cells. This modulation helps create a favorable environment for neuroprotection and repair.
Paracrine effects: MSCs secrete a variety of bioactive factors that exert beneficial effects on neighboring cells. These factors can promote tissue repair, angiogenesis, and the formation of new blood vessels, which may enhance the microenvironment for motor neuron survival.
Therapeutic benefits observed in preclinical and clinical studies of MSC treatment for ALS include:
Slowing disease progression: MSC treatment has shown potential in slowing the progression of ALS, as evidenced by improvements in disease markers and motor function in some patients.
Extended survival: Some studies have reported prolonged survival in ALS patients who received MSC treatment compared to those who did not receive the treatment.
Improved motor function: MSC therapy has been associated with improvements in muscle strength, motor skills, and functional capacity in ALS patients. These improvements can enhance quality of life and prolong independent living.
Reduced neuroinflammation: MSCs’ anti-inflammatory properties can reduce neuroinflammation in ALS patients, potentially slowing disease progression and preserving motor function.
We organize our stem cell packages based on the size and complexity of your condition. Small, simple conditions require relatively few stem cells to treat them. Large, complicated conditions— or conditions you wish to treat as quickly and as completely as possible—will require larger volumes of stem cells to get the job done.
Our price for this treatment starts at $19.500 (US Dollar). The treatment duration is between 3-5 days depending on your specific condition.
Details | Treatment Type | Stem Cell Volume |
I | Single Area of Focus & Treatment | 50,000,000 stem cells |
II | Multiple Areas of Focus, Simple Inflammatory Conditions, or Early Stage Disease | 100,000,000 stem cells |
III | Complex Conditions or Premium Option for Simple Conditions | 200,000,000 stem cells |
IV | Advanced Stage Disease or Fastest Possible Treatment for All Conditions | 300,000,000+ stem cells |
We select your supportive therapies based on your condition. Your supportive therapies will direct your stem cells to the impacted tissue that needs to be regenerated, trigger selective cell activity, and provide your body with additional biological building blocks to deliver a faster and more complete regeneration.
We offer many supportive therapies, that include but are not limited to:
- Peptides & Messenger RNA
- Laser Blood Irradiation
- Laser Tissue Radiation
- Shockwave Therapy
- Ozone or Oxygenation
- NAD+
- Physiotherapy
- Nutrition & Enzymes
We curate an additional set of simple supportive therapies that you will bring home with you after your treatment, and self-administer for one to three months. This take home set ensures that your stem cells and your impacted tissue continue to receive direction and building blocks to continue to regenerate after your initial treatment.
We typically provide a one to three-month supply of:
- Compounded Nutrition
- Messenger RNA
- Growth Factors






