What Are Stem Cells
Stem Cells Characteristics:
STEM CELLS are like the building blocks of the human body. At the beginning of our lives, they divide over and over again to create us from an embryo. During our lifetime, they replenish cells in our blood, bone, skin, and organs to keep us alive and functioning. Stem cells hold 2 main characteristics which stand them out from other cell types in our bodies:
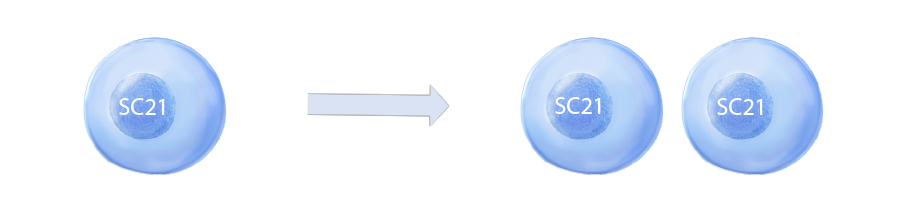
- Firstly, the ability to self-renew (perform mitosis), this is a part of the cell cycle when replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. This gives rise to identical replicated cells.
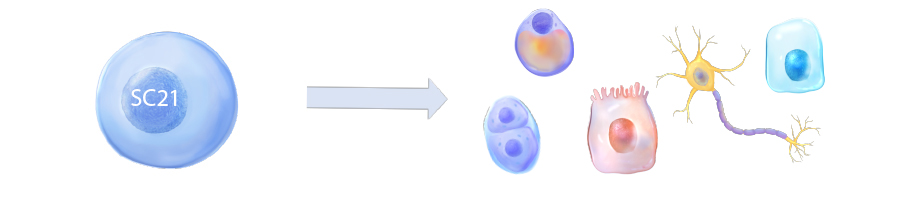
- Secondly, the ability to differentiate into specialized cells such as cartilage, heart cells, liver cells, and neurons. No other cell in the body has the natural ability to generate new cell types.
Types of Stem Cells
Pluripotent
Source: Embryonic or Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Ability: Capable of giving rise to every cell type in the human body with unlimited self-renewal.
Multi-potent
Source: Adult or Fetal Tissue and Blood
Ability: Capable of giving rise to most cell types in the human body with limited self-renewal.
Progenitor
Source: Adult or Fetal Tissue and Blood
Ability: Capable of giving rise to a few cell types in the human body with limited self-renewal.
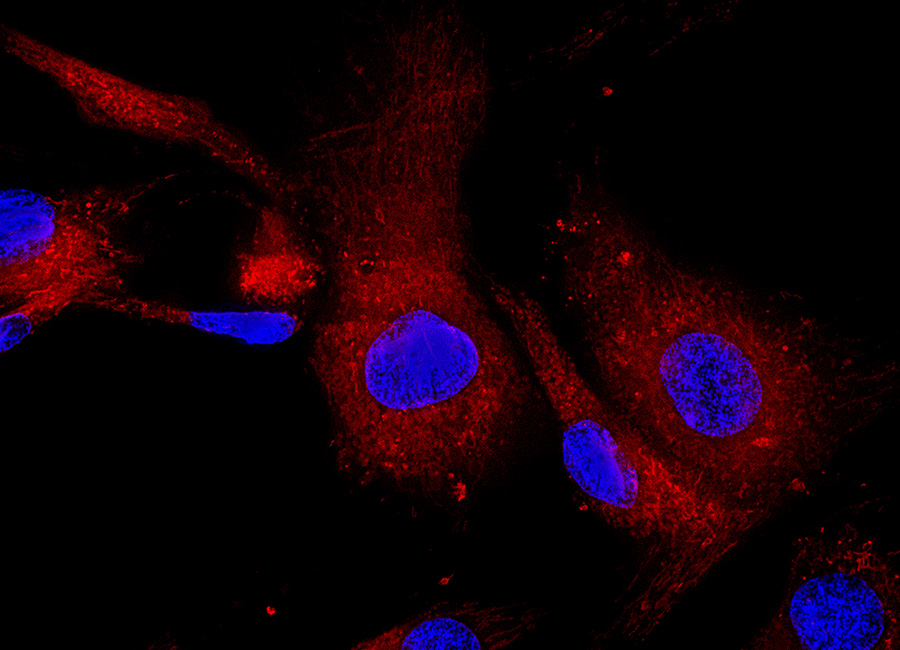
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are multi-potent stem cells found in various Fetal and adult tissues. MSCs have differentiation, self-renewal capacity, regenerative and immune-modulation function. MSCs differentiate into osteogenic-, adipogenic-, chondrogenic- and other cells. MSCs in many situations, such as disease treatment, is full of exciting possibilities.
Immune Modulation:
They have the ability to modulate immune responses and control inflammation.
Stimulatory Secretions:
They produce a range of various stimulatory secretions that aid in repair and regeneration.
Repopulation of Stem Cell Pools:
Newly introduced Cells with young biological age can repopulate our cell pools.






